Контроллер доступа AC6605
Контроллер доступа AC6605-26-PWR Huawei объединяет в себе функциональность Ethernet-коммутатора 1000M для управления как проводным, так и беспроводным доступом. AC6605-26-PWR предлагает пользователям множество возможностей при настройке точек доступа (AP). Используемый совместно с точками доступа Huawei премиум класса, точками доступа улучшенного класса и стандартными точками доступа Huawei, AC6605-26-PWR предлагает сетевое решение корпоративного класса для сетей кампусного типа, промышленных сетей, a также корпоративных сетей малого и среднего масштаба. При этом происходит расширение зоны действия "горячих" точек.

Множество типов портов
Восходящие порты: два оптических порта 10 GE.
Порты услуг: 24 порта GE, последние четыре порта могут работать в совмещенной оптическом режиме
Порты обслуживания: Один последовательный порт обслуживания RJ45; Один порт обслуживания Ethernet RJ45; Один последовательный порт обслуживания мини-USB.
Высокая емкость и производительность, интегрированный дизайн
Интегрированный дизайн: в оборудовании AC6605 интегрированы AC и LSW, чтобы обеспечить функции доступа и агрегацию.
Высокая емкость: AC6605 имеет 24 порта GE и 2 порта 10GE, что обеспечивает емкость коммуатции 128 Гбит/с.
Поддержка питания через Ethernet (PoE)
Надежность операторского класса
Поддержка резервирования портов на основе протокола управления агрегацией соединения (LACP) и протокола множественного связующего дерева (MSTP).
Поддержка двойного резерва источника питания постоянного/переменного тока.
Блок питания допускает «горячую замену» во время работы.
Простота установки и обслуживания
Размеры AC6605 442 мм × 420 мм × 44.4 мм позволяют устанавливать его в стандартный статив.
Блок питания допускает «горячую замену» во время работы, что облегчает обслуживание.
Коммутатор AC6605 может администрироваться при помощи eSight и обеспечиваетразличные восходящие интерфейсы.
Коммутатор AC6605 поддерживает порт Boolean, для мониторинга окружающей среды и измерения температуры внутренней платы.
Функции и спецификации коммутатора LAN (LSW)
| Функция | Описание | |
| Ethernet features | Ethernet | Operating modes of full duplex, half duplex, and auto-negotiation Rates of an Ethernet interface: 10 Mbit/s, 100 Mbit/s, 1000 Mbit/s, and auto-negotiation Flow control on interfaces Jumbo frames Link aggregation Load balancing among links of a trunk Interface isolation and forwarding restriction Broadcast storm suppression |
| VLAN | Access modes of access, trunk, hybrid, and QinQ Default VLAN VLAN mapping Selective QinQ Voice VLAN | |
| MAC | Automatic learning and aging of MAC addresses Static, dynamic, and blackhole MAC address entries Packet filtering based on source MAC addresses Interface-based MAC learning limiting | |
| ARP | Static and dynamic ARP entries ARP in a VLAN Aging of ARP entries | |
| Smart Link | Smart Link Smart Link multi-instance Monitor Link | |
| LLDP | LLDP | |
| Ethernet loop protection | MSTP | STP RSTP MSTP BPDU protection, root protection, and loop protection Partitioned STP and BPDU tunnels |
| RRPP | RRPP protective switchover Single RRPP ring, tangent RRPP ring, and intersecting RRPP ring Hybrid networking of RRPP rings and other ring networks | |
| IPv4/IPv6 forwarding | IPv4 features | ARP and RARP ARP proxy Auto-detection |
| Unicast routing features | Static route RIP-1 and RIP-2 OSPF BGP IS-IS Routing policies and policy-based routing URPF check VRF DHCP client,server and relay DHCP snooping | |
| Multicast routing features | IGMPv1, IGMPv2, and IGMPv3 PIM-SM Multicast routing policies RPF | |
| IPv6 features | IPv6 protocol stack IPv6 unicast routing protocols: RIPng and OSPFv3 VRRP6 IPv4/IPv6 transition technologies | |
| Device reliability | BFD | Basic BFD functions BFD for OSPF BFD for IS-IS BFD for BGP BFD FOR PIM |
| Others | VRRP | |
| Layer 2 multicast features | Layer 2 multicast | IGMP snooping Prompt leave Multicast traffic control Inter-VLAN multicast replication Controllable multicast |
| Ethernet OAM | EFM OAM | Neighbor discovery Link monitoring Fault notification Remote loopback |
| CFM OAM | CCM check MAC ping MAC trace | |
| Y.1731 | Delay and variation measurement | |
| QoS features | Traffic classification | Traffic classification based on the combination of the L2 protocol header, IP 5-tuple, outbound interface, and 802.1p priority Traffic classification based on the C-VID and C-PRI of QinQ packets |
| Action | Access control after traffic classification Traffic policing based on traffic classification Re-marking packets based on traffic classifiers Class-based packet queuing Associating traffic classifiers with traffic behaviors | |
| Queue scheduling | PQ scheduling DRR scheduling PQ+DRR scheduling WRR scheduling PQ+WRR scheduling | |
| Congestion avoidance | SRED WRED | |
| Rate limiting on outbound interfaces | Rate limiting on outbound interfaces | |
| Configuration and maintenance | Terminal service | Configurations using command lines Error message and help information in English and Chinese Login through console and Telnet terminals Send function and data communications between terminal users |
| File system | File systems Directory and file management File uploading and downloading using FTP and TFTP | |
| Debugging and maintenance | Unified management over logs, alarms, and debugging information Electronic labels User operation logs Detailed debugging information for network fault diagnosis Network test tools such as traceroute and ping commands Interface mirroring and flow mirroring | |
| Version upgrade | Device software loading and online software loading BootROM online upgrade In-service patching | |
| Security and management | System security | Different user levels for commands, preventing unauthorized users from accessing AC6605 SSHv2.0 RADIUS and HWTACACS authentication for login users ACL filtering DHCP packet filtering (with the Option 82 field) Defense against control packet attacks Defenses against attacks such as source address spoofing, Land, SYN flood (TCP SYN), Smurf, ping flood (ICMP echo), Teardrop, and Ping of Death attacks |
| Network management | ICMP-based ping and traceroute SNMPv1, SNMPv2c, and SNMPv3 Standard MIBRMON | |
Функции и спецификации AC
Функции и спецификации AP
| Функция | Спецификации |
| AP access control | Displays MAC addresses or SNs of APs in the whitelist. Adds a single AP or multiple APs (by specifying a range of MAC addresses or SNs) to the whitelist. Automatically discovering and manually confirming APs. Automatically discovering APs without manually confirming them. |
| AP region management | Supports three AP region deployment modes: Distributed deployment: APs are deployed independently. An AP is equivalent to a region and does not interfere with other APs. APs work at the maximum power and do not perform radio calibration. Common deployment: APs are loosely deployed. The transmit power of each radio is less than 50% of the maximum transmit power. Centralized deployment: APs are densely deployed. The transmit power of each radio is less than 25% of the maximum transmit power. Specifies the default region to which automatically discovered APs are added. Supports a maximum of 256 AP regions with a region description of 63 characters. |
| AP profile management | Specifies the default AP profile that is applied to automatically discovered APs. Supports a maximum of 256 AP profiles. |
| AP type management | Manages AP attributes including the number of interfaces, AP types, number of radios, radio types, maximum number of virtual access points (VAPs), maximum number of associated users, and radio gain (for APs deployed indoors). Provides default AP types. Supports user-defined AP types. Supports a maximum of 256 AP types. |
| Network topology management | Supports LLDP topology detection. |
Спецификации управления радиоканалом
| Функция | Спецификации |
| Radio profile management | The following parameters can be configured in a radio profile: Radio working mode and rate Automatic or manual channel and power adjustment mode Radio calibration interval The radio type can be set to 802.11n, 802.11b/g/n, or 802.11a/n. You can bind a radio to a specified radio profile. A maximum of 1024 radio profiles are supported. |
| Unified static configuration of parameters | Radio parameters such as the channel and power of each radio are configured on the AC and then delivered to APs. |
| Dynamic management | APs can automatically select working channels and power when they go online. In an AP region, APs automatically adjust working channels and power in the event of signal interference: Global calibration: The optimal working channel and power of a specified AP can be adjusted. Partial calibration: The optimal working channels and power of all the APs in a specified region can be adjusted. When an AP is removed or goes offline, the AC6605 increases the power of neighboring APs to compensate for the coverage hole. Automatic selection and calibration of radio parameters in AP regions are supported. |
| Enhanced service capabilities | The AC6605 supports 802.1a/b/g/n. These modes can be used independently or jointly (a/n, b/g, b/g/n, and g/n). That is, a total of eight modes can be used. The AC6605 preferentially uses the 5 GHz frequency band for STAs. |
Спецификации администрирования услуг WLAN
| Функции | Спецификации |
| ESS management | Allows you to enable SSID broadcast, set the maximum number of access users, and set the association aging time in an ESS. Isolates APs at Layer 2 in an ESS. Maps an ESS to a service VLAN. Associates an ESS with a security profile or a QoS profile. Enables IGMP for APs in an ESS. Configures a maximum of 1024 ESSs. |
| VAP-based service management | Adds multiple VAPs at a time by binding radios to ESSs. Displays information about a single VAP, VAPs with a specified ESS, or all VAPs. Supports configuration of offline APs. Creates VAPs according to batch delivered service provisioning rules in automatic AP discovery mode. Supports up to 20000 VAPs. |
| Service provisioning management | Supports service provisioning rules configured for a specified radio of a specified AP type. Adds automatically discovered APs to the default AP region. The default AP region is configurable. Applies a service provisioning rule to a region to enable APs in the region to go online. Supports a maximum of 256 service provisioning rules. |
| Multicast service management | Supports IGMP snooping. Supports IGMP proxy. |
| Load balancing | Performs load balancing among radios in a load balancing group. Supports two load balancing modes: Based on the number of STAs connected to each radio Based on the traffic volume on each radio |
Качество услуг QOS
| Функция | Спецификации |
| WMM profile management | Enables or disables Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM). Supports a maximum of 32 WMM profiles. Allows a WMM profile to be applied to radios of multiple APs. |
| Traffic profile management | Manages traffic from APs and maps packet priorities according to traffic profiles. Supports a maximum of 32 traffic profiles. Applies a QoS policy to each ESS by binding a traffic profile to each ESS. |
| AC traffic control | Manages QoS profiles. Uses ACLs to perform traffic classification. Limits the incoming traffic rate on each physical port based on inbound CAR parameters and limits the outgoing traffic rate based on outbound CAR or traffic shaping parameters. Limits incoming and outgoing traffic rates for each user based on inbound and outbound CAR parameters. Limits the traffic rate based on ESSs or VAPs. |
| AP traffic control | Controls traffic of multiple users and allows users to share bandwidth. Limits the rate of a specified VAP. |
| Packet priority configuration | Sets the QoS priority (IP precedence or DSCP priority) for CAPWAP control channels. Sets the QoS priority for CAPWAP data channels: Allows you to specify the CAPWAP header priority. Maps 802.1p priorities of user packets to ToS priorities of tunnel packets. |
Спецификации безопасности WLAN
| ФУНКЦИЯ | Спецификации |
| WLAN security profile management | Manages authentication and encryption modes using WLAN security profiles. Binds security profiles to ESS profiles. Supports a maximum of 256 AP profiles. |
| Authentication modes | Open system authentication with no encryption WEP authentication/encryption WPA/WPA2 authentication and encryption: WPA/WPA2-PSK+TKIP WPA/WPA2-PSK+CCMP WPA/WPA2-802.1x+TKIP WPA/WPA2-802.1x+CCMP WAPI authentication and encryption: Supports centralized WAPI authentication. Supports three-certificate WAPI authentication, which is compatible with traditional two-certificate authentication. Issues a certificate file together with a private key. Allows users to use MAC addresses as accounts for authentication by the RADIUS server. Portal authentication: Allows an AC to function as a portal gateway. Prohibits an AC from functioning as a portal gateway. Supports only Layer 2 portal. |
| Combined authentication | Combined MAC authentication: PSK+MAC authentication MAC+portal authentication: MAC authentication is used first. When MAC authentication fails, portal authentication is used. This type of authentication applies only to centralized forwarding. |
| AAA | Local authentication/local accounts (MAC addresses and accounts) RADIUS authentication Multiple authentication servers: Supports backup authentication servers. Specifies authentication servers based on account. Configures authentication servers based on account. Binds user accounts to SSIDs. |
| Security isolation | Port-based isolation User group-based isolation |
| Authority control | ACL limit based on the following: Port User group User |
| Other security features | SSID hiding IP source guard: Configures IP and MAC binding entries statically. Generates IP and MAC binding entries dynamically. |
Спецификации администрирования пользователей WLAN
Функции администрирования и обслуживания
| Тип | Функция |
| Management | Debugging through the serial port or Ethernet port |
| Remote configuration using Telnet | |
| Device configuration using the CLI | |
| Device management using the U2560 | |
| System log | |
| Alarms with different severities | |
| Maintenance | Debugging information output |
| Ping | |
| Remote maintenance using SSH or Telnet | |
| Version management | Providing three methods to load version files to APs: Save the version files on APs. Send version files to APs through the control tunnels. Transfer version files to APs using FTP. |
| Checking and configuring mappings between AP types and version files so that APs can download version files automatically | |
| Manually downloading version files to APs of a specified type in batches and querying the download result |
| Параметр | Описание | |
| Dimensions (width x depth x height) | 442 mm x 420 mm x 44.4 mm | |
| Maximum power consumption | 85 W | |
| Weight | Net weight: 5.48 kg Fully configured with 150 W power supplies: 7.16 kg Fully configured with 500 W power supplies: 7.48 kg | |
| Operating temperature | -5ºC to +50ºC | |
| Relative humidity | 5% RH to 95% RH, non-condensing | |
| Operating altitude | 150 W DC power supply: 0 m to 2000 m Others: 0 m to 3000 m | |
| AC input voltage | Rated voltage | 100 V AC to 240 V AC, 50/60 Hz |
| Voltage range | 90 V AC to 264 V AC, 47/63 Hz | |
| DC input voltage | Rated voltage | -48 V DC to -60 V DC |
| Voltage range | -36 V DC to -72 V DC | |
Конфигурация системы
Свойства протоколов управления
Спецификации протоколов
| Параметр | Спецификация |
| Number of MAC addresses | 32 K for an LSW and 16 K for an AC |
| Number of VLANs | 4K |
| Number of ARP entries | 16 K for an LSW and 8 K for an AC |
| Number of routing entries | 12 K for an LSW and 8 K for an AC |
| Number of multicast forwarding entries | 2 K for an LSW and 4 K for an AC |
| Number of DHCP IP address pools | On an LSW: 128 IP address pools, each of which contains a maximum of 8 K IP addresses On an AC: 128 IP address pools, each of which contains a maximum of 16 K IP addresses |
Возможности беспроводной сети
| Функция | Спецификации |
| Networking between APs and ACs | APs and ACs can be connected through a Layer 2 or Layer 3 network. APs can be directly connected to an AC and powered by a 24-port PoE switch. ACs can function as both access and aggregation switches. APs are deployed on a private network, while ACs are deployed on the public network to implement NAT traversal. ACs can be used for Layer 2 bridge forwarding or Layer 3 routing. |
| Forwarding mode | Direct forwarding (distributed forwarding or local forwarding) Tunnel forwarding (centralized forwarding) Centralized authentication and distributed forwarding Before users are authenticated, tunnel forwarding is used. After users are authenticated, local forwarding is used. |
| Wireless networking mode | WDS bridging: Point-to-point (P2P) wireless bridging Point-to-multipoint (P2MP) wireless bridging Automatic topology detection and loop prevention (STP) |
| AC discovery | An AP can obtain the AC6605's IP address in any of the following ways: Static configuration DHCP Option 43 DNS The AC6605 uses DHCP to allocate IP addresses to APs. Huawei APs are identified by the Option 60 field. DHCP relay is supported. On a Layer 2 network, APs can discover the AC6605 by sending broadcast or multicast CAPWAP packets. |
| CAPWAP tunnel | Centralized CAPWAP CAPWAP control tunnel and data tunnel (optional). CAPWAP tunnel forwarding and direct forwarding in an extended service set (ESS). Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) encryption, which is enabled by default for the CAPWAP control tunnel Heartbeat detection and tunnel reconnection. |
| Active and standby ACs | Enables and disables the switchback function. Supports load balancing. Supports 1+1, N+1, and N+N backup. |
Сценарии применения
AC6605 подключается к коммуатору агрегации в режиме цепи или звезды.
AC6605 обрабатывает как управляющие сигналы так и потоки данных. Потоки управления должны передаваться через туннели CAPWAP (Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points). Потоки данных могут передаваться как через туннели CAPWAP, так и без них.
Протокол CAPWAP определяет, как точка доступа AP связывается с контроллером ACs и обеспечивает механизм основной инкапсуляции, так и механизм для связи между AP и AC. CAPWAP определяет туннели данных и управляет ими.
Туннели данных инкапсулируют пакеты данных 802.11, которые передаются через AC6605.
Туннели управления передают управляющие потоки для удаленной конфигурации AP и администрирования WLAN.
Два режима пересылки (forwarding ) доступны, в зависимости от того, как данные передаются по туннелям CAPWAP:
Прямая пересылка: также она называется местной или распределенной пересылкой.
Туннельная пересылка: также называется централизованной пересылкой. Обычно используется для трафиком управления беспроводных полльзователей централизованным образом.
В завимости от требований сети, можно использовать цепной или звездчатый режим подключения точек доступа. На AC6605 можно сконфигурировать прямую пересылку для одних точек доступа AP и туннельную пересылку для других AP. В туннельном режиме пересылки весь трафик беспроводных пользователей будет агрегироваться в АС, что может приводить к перегрузке коммутации. Поэтому, туннельная пересылка для целей предприятий используется нечасто.
Цепное построение сети
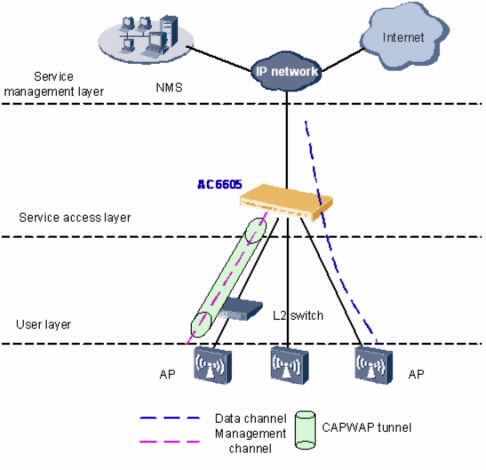
При цепном подключении, AP или коммутаторы доступа напрямую подключаются к AC6605. AC6605 функционирует как AC и как коммутатор агрегации для пересылки и обработки данных AP и администрирования услуг.
В цепном режиме, AC6605 устанавливает туннели CAPWAP с точками доступа AP для конфигурирования и администрирования этих AP по туннелям CAPWAP. Данные услуг беспроводных пользователей могут пересылаться между точками AP и AC6605 через туннель CAPWAP или пересылаться от AP напрямую.
В цепном режиме подключения часто используется прямая пересылка, таким образом, данные услуг пользователя могут напрямую пересылаться в AP.
AC6605 может работать как DHCP-сервер для размещения IP-адресов на AP. AP получают IP-адрес от AC6605 при помощи функции DNS, DHCP Option 43 в DHCP-пакетах, или протоколе обнаружения сети L2, и затем устанавливают туннели данных с AC6605.
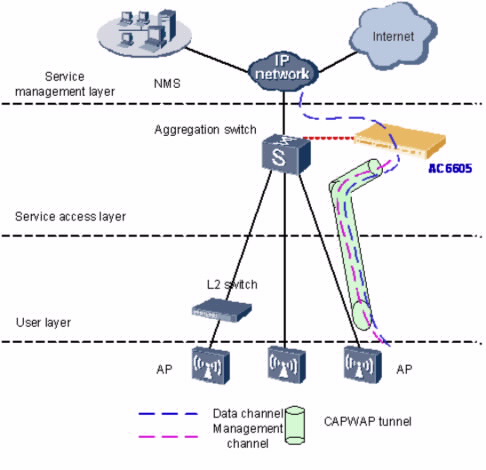
В режиме прямой пересылки, контролируются только потоки передаваемые по туннелям CAPWAP, и потоки данных, посылаемые от AP, прозрачно передаются в вышестоящее устройство через AC6605, как показано на рисунке. Потоки данных идентифицируются VLAN ID.
Когда потоки данных передаются по туннелям CAPWAP, нужно сконфигурировать VLAN VLAN данных следующим образом:
На AC6605 и его восходящих коммутаторах, нужно сконфигурировать VLAN администрирования AC для передачи потока данных между AC6605 и NMS.
На коммутаторах между AP и AC6605, нужно сконфигурировать VLAN администрирования AC для передачи потоков управления между AP и AC6605.
На всех коммутаторах между точками доступа AP и BRAS, нужно сконфигурировать VLAN данных для того, чтобы отличить их от потоков услуг WLAN.
AC6605 иметт проводное коммутирующее устройство, которое обеспечивает эффективный доступ и агрегацию. Кроме того, AC6605 обеспечивает питание PoE+ для 24 интерфейсов Ethernet, поэтому AP могут напрямую подключаться к AC6605. Прямая переслка часто используется в цепном режиме построения сети. Этот сетевой режим упрощает архитектуру сети и используется для централизованный WLAN большой емкости.
Централизованное построение сети
В централизованном режиме, AC6605 подключается к сетевому устройству (обычно агрегационному коммутатору) для управления AP.
AC6605 только управляет AP. Потоки управления передаются по туннелям CAPWAP, а потоки данных пересылаются на верний уровень сети коммутатором агрегации, и BRAS и не проходят через AC6605.
Прямая пересылка
В режиме прямой пересылки, данные от беспроводного пользователя транслируются из пакетов 802.3 в пакеты 802.11, которые затем передаются коммутатором агрегации восходящего потока.
Централизованный режим построения сети часто используется в сетях предприятий. Данные услуг беспроводного пользователя могут не обрабатываться в AC, устраняя тем самым "узкое место" коммутации в сети, и облегчая тем самым, использование политик безопасности. Таким образом, рекомендуется именно этот режим построения сети.
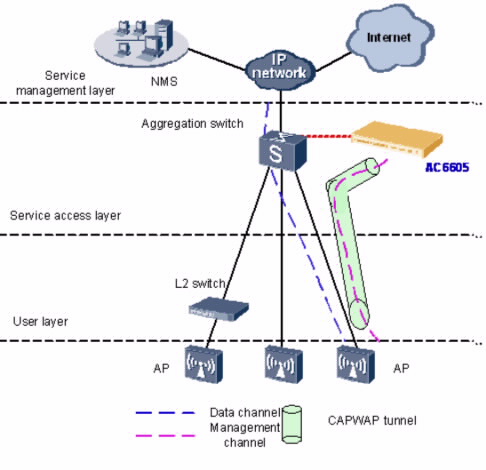
AC6605 только управляет APs. Все потоки управления AP должны проходить через AC6605.
Коммутатор агрегации имеет порт для подключения к AC6605 и работает как DHCP-сервер размещающий IP-адреса для AP. AP получает IP-адреса AC6605 используя потки DNS обеспечиваемые BRAS или DHCP Option 43 в пакетах DHCP.
Данные от точек доступа AP передаются коммутатором Layer 2, коммутатором агрегации, и BRAS и не проходят через AC6605.
Различные VLAN предписываются STA с различными наборами идентификаторов (SSID). Коммутатор Layer 2 и коммутатор агрегации идентифицирует пакеты от этих VLAN и передает эти пакеты на BRAS. BRAS терминирует пакеты, управляет доступом пользоватнля, и размещает IP-адреса для пользователей. После того, как пользователь был аутентифицирован BRAS, трафик пользователя передается в Интернет через IP-сеть.
Пересылка по туннелю
В режиме пересылки по туннелю, данные услуг беспроводного пользователя переадются между точками доступа AP и контроллером AC через туннели CAPWAP.
На рисунке, потоки данных и потоки управления от точек доступа APs передаются на AC6605 через туннели CAPWAP, и затем AC6605 прозрачно передает эти потоки на вышестоящее устройство.
Туннельная пересылка обычно используется для управления трафиком беспроводного пользователя централизованным образом. Этот режим пересылки облегчает развертывание устройств и контрлирует все пользователей беспроводного доступа, подключенных к АР и далее к АС по туннелю CAPWAP.