Solución de red troncal extranet de e-Government provincial de múltiples planos
New services, such as unified communications, remote video conferences, and collaborative offices, bring more opportunities and challenges to government networks. The need for higher bandwidth and advanced services within government organizations has spurred demand for national e-Government extranets.
To solve these challenges, Huawei offers a multi-plane e-Government backbone network solution. This solution uses virtualization and MPLS VPN technologies in the backbone network architecture to meet government requirements for security protection, service deployment, and system management.
Requirements and Challenges
The central government of the People's Republic of China (PRC) authorized the development of e-Government networks to provide network, information, and security support for individual departments, and to facilitate office and public services.
An e-Government extranet solution was required to meet the service requirements of the layered government administration: The provincial e-Government extranet connects to both the upper-level national and lower-level municipal and county-level e-Government extranets. The e-Government extranet enables data sharing and service collaboration across departments.
The Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN), Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) Virtual Private Network (VPN), and multi-Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) technologies supply network access control and data channel isolation. To meet the security needs of individual departments, each VPN performs internal security controls according to its own internal security policies, which requires data centers within VPNs to accept external data streams and transfer data streams between regions with different security levels. Because security requirements vary among VPNs, a security device divided into several logical ones was considered to better meet access control requirements.
A provincial e-Government extranet backbone network solution had the following requirements:
Full network coverage
A provincial e-Government extranet backbone network must support access by all levels of government (provincial, municipal, and county). The backbone network must also support access by provincial data centers and provincial government agencies, including provincial departments, local departments under the direct administration of the central government, colleges and universities, and large-sized state-owned enterprises.
Provincial backbone networks include provincial, municipal, and county-level nodes. Horizontally, nodes of each level connect to the core routers of the same level. For example, provincial nodes connect to provincial core routers, and municipal nodes connect to municipal core routers. Vertically, nodes connect to provincial, municipal, and county-level core routers to enable access to networks at all levels using extranets.
Service security isolation
The e-Government extranet bears services for multiple departments; however, service isolation is required to enable independent operation, management, and security protection. A traditional MPLS VPN cannot ensure secure service isolation.
To enhance service security, e-Government needs advanced router virtualization technology to divide a physical network into several virtual network platforms for bearing services for different departments, enabling each department to operate independently and securely.
Dynamic bandwidth adjustment
The provincial e-Government extranet backbone network must support flexible vertical bandwidth adjustment and balancing, which means that the backbone manages network resource allocations, controls access to existing government-level networks, and quickly deploys applications to all levels as required.
High reliability and integration
The backbone network must provide high stability to ensure routine data transmission and communications for services in network environments. The network also needs high compatibility to integrate different vendors' applications and technologies.
Solution Description
Huawei provides the sophisticated and comprehensive multi-plane provincial e-Government extranet backbone network solution to meet the specific needs of government. The solution is detailed in the following sections.
Networking Design
The Multi-Plane e-Government Extranet Backbone Network solution uses advanced router virtualization and MPLS VPN technologies to build a multi-plane, provincial e-Government extranet backbone network that offers these features:
Flexible access to provincial, municipal, and county-level metropolitan area networks (MANs)
-The solution makes full use of the existing network to minimize impacts on department administration services.
-The solution integrates existing MANs into the system. The core routers of the MANs directly connect to the core routers of the same-level WANs and serve as core access nodes.
-The system connects the networks of departments that do not have private MANs to the core nodes of the same level MAN using private MAN lines.
Flexible access to department VPNs at all levels
The solution requires only minimal modification to existing private network WANs and connects these private networks to core nodes of the same level WANs to enable cross-department data sharing.
Huawei provides differentiated network planes for provincial departments, offering virtual network planes for departments that have higher security requirements and MPLS VPN network planes for more public departments.
Network isolation
The network isolation mechanism ensures that administration services are not interrupted by network conditions. If the network is disconnected from the Internet, administration services are not affected. Provincial and municipal e-Government extranets have unified Internet egress points for managing Internet traffic as well as one or more backup links.
Dynamic bandwidth adjustment
Service-based dynamic bandwidth adjustment improves bandwidth resource usage and meets bandwidth growth requirements. Links that connect the core devices of backbone networks support the load balancing function. For example, a county-level core node connects to the municipal core node and uses two links to support the load balancing function.
Virtual network plane management
Different network planes bear services for different government departments. Network planes are independent of each other. Government departments can manage planes, view virtual network resource usage, manage network quality, and control bandwidth within planes.
Efficient use of existing devices
The solution uses existing network devices, such as the core routers and switch devices in MANs and private networks of government departments, as convergence devices and connects these devices to core routers in all levels of e-Government extranets.
Solution Design
Huawei provides comprehensive routers for departments at each level to enable the vertical interconnection in the backbone network. Provincial core nodes use the high-end NE5000E-X16, municipal nodes use the NE20E-S8, and county-level nodes use NE20E-S4 as core routers. The following figure shows the network architecture of the e-Government solution.
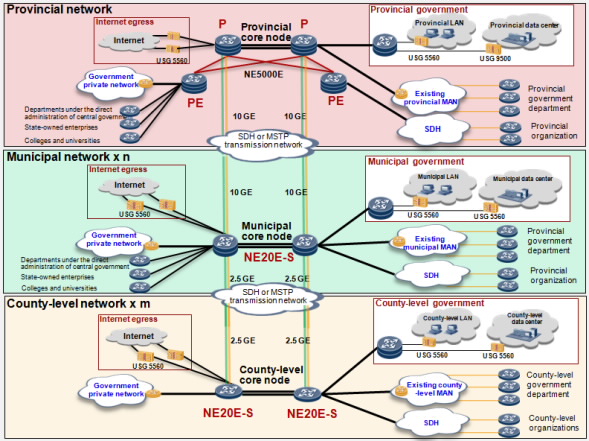
Figure 1:Provincial e-Government backbone network solution architecture
- Transmission links
- Provincial-municipal WAN links
- Cross-department access links
- Provincial core nodes
- Municipal core nodes
- County-level core nodes
- Load balancing
- QoS
- Reliability
The solution uses two types of links as WAN backbone links and MAN access links: Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) and Multi-Service Transmission Platform (MSTP). SDH is the most widely deployed technology for optical transmission links. MSTP technology is based on SDH and can bear automatic teller machine (ATM) and Ethernet services and includes multiple types of Ethernet interfaces.
SDH links require user-end routers to support Channelized Packet over SDH/SONET (CPOS) interfaces and require client bandwidth to exceed 155 Mbit/s. At bandwidth speeds lower than 155 Mbit/s, optical transceivers and protocol converters are required to enable the connection between the client and transmission network. The SDH supports switching between a limited number of bandwidth levels, including 155 Mbit/s, 622 Mbit/s, 2.5 Gbit/s, and 10 Gbit/s.
The MSTP uses FE and GE interfaces to connect to user-end routers without special requirements. The MSTP also supports switching between multiple bandwidth levels, such as 10 Mbit/s, 100 Mbit/s, and 1,000 Mbit/s, which enables flexible network bandwidth adjustment. The MSTP provides distinct advantages at the access and convergence layers of MANs. In addition to IP, ATM, and SDH service support, the MSTP supports statistics and reuse of service data, which adds efficiency to bandwidth usage.
Provincial and municipal nodes use SDH links. Two provincial core routers use two 155 Mbit/s Packet over SONET/SDH (POS) downstream links and two municipal core routers use one 155 Mbit/s POS upstream link to connect to the SDH transmission network. The POS upstream link can be expanded to 622 Mbit/s.
Municipal-county WAN links
The solution uses MSTP to build links between the municipal and county-level nodes if MSTP links are available, which enables bandwidth adjustment based on service requirements, reducing bandwidth leasing costs. If no MSTP link is available, the solution uses SDH. Two municipal core routers use two 155 Mbit/s POS downstream links to connect to the SDH transmission network. County-level core routers use one or more 155 Mbit/s POS upstream links to connect to the SDH transmission network based on service requirements. The POS upstream links can be expanded to 622 Mbit/s.
The solution uses private MSTP links to perform cross-department connection. Two provincial core PE routers use 10 GE MSTP links to connect to the transmission network. The MSTP supports the virtual link function, such as Ethernet Virtual Private Line (EVPL). One EVPL can bear multiple virtual SMTP links, which enables the access link convergence of provincial core PE routers in MANs (using the VLAN to separate virtual links) and reduces the quantity of ports on PE routers.
Municipal core routers use 10 GE MSTP private links and county-level core routers use 1 GE MSTP private links to connect to the transmission network with virtual link functions enabled.
The provincial clients connect to core PE routers using private links with bandwidths of 2 Mbit/s, 10 Mbit/s, or higher.
Provincial core nodes use dual-core high-end 10 GE routers. The routers support the virtualization technology that enables one set of NE5000E devices to be divided into multiple virtual routers. The solution uses virtual routers to bear e-Government extranet and private network services separately and perform security isolation on multiple layers, including the physical layer (such as boards and ports), router control and data transmission layer, and management and configuration layer.
The solution implements provincial core nodes in P + PE mode. P nodes connect to provincial government departments, data centers, MANs, and Internet egresses. PE nodes connect to municipal department networks under the direct administration of the provincial government, provincial departments under the direct administration of the central government, provincial government private networks, state-owned enterprises, and colleges and universities.
Provincial core nodes connect to municipal backbone network core nodes using P devices.

Figure 2:Provincial core node architecture
The solution deploys two sets of NE20E-S8 devices in municipal core nodes, enabling municipal core nodes to work as core P nodes and connect to provincial core routers. Both active and standby links provide 155 Mbit/s bandwidth.
PE devices connect to municipal data centers, government departments, government private networks, departments under the direct administration of central government, and colleges and universities.

Figure 3:Municipal core node architecture
Each county-level core node has one set of NE20E-S4 or NE20E-S4 devices and works as a core P node. The solution uses the S7700 as the core PE device, enabling county-level core nodes to connect to county-level government departments, data centers, and government private networks.

Figure 4:County-level core node architecture
The backbone network core routers forward data on the MPLS network. Routers use the Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) to establish Label Switched Path (LSP) routes and forward packets using the LSP on the MPLS network.
Links that connect core devices of backbone networks support the load balancing function. In the preceding figure, the county-level core node connects to the municipal core node using two links that support the load-balancing function.
The e-Government network supports multiple co-existing services and requires QoS technologies to ensure that key services can have differentiated (better) QoS support. The solution uses multiple QoS technologies, such as priority mapping, traffic control, traffic shaping, queue adjustment, and traffic jam prevention, to improve the network QoSs by taking into account bandwidth, delay, jitter, and packet loss rate. This feature improves the user experience when multiple services are deployed and bandwidth resources are limited.
The e-Government extranet uses the backbone network to implement QoS policies. The backbone network uses the Diff-Serv model to provide differentiated services for different types of traffic.
The e-Government extranet backbone network uses Border Gateway Patrol (BGP) and MPLS IP VPN technologies. Huawei deploys MPLS Hierarchical Quality of Service (HQoS) to provide a comprehensive VPN QoS solution. HQoS satisfies the diversified and refined QoS requirements for VPN users by:
Providing layered QoS (L2VPN and L3VPN) on the backbone network based on the PE and VPN instances.
Providing layered QoS (L2VPN, L3VPN, and MVPN) on the backbone network based on VPN instances.
Providing layered QoS (L2VPN and L3VPN) on the interfaces of VPN-instance CEs.
The solution implements layered QoS on the backbone network side according to VPN instance. The QoS technology specifies bandwidth and service priorities based on VPN instances on PEs; for example, the bandwidth of a VPN is 30 Mbit/s. The VPN distributes more bandwidth to services with higher priorities, such as video services. On the PE side, services are queued based on service priorities on the VPN to ensure and control bandwidth availability and distribution on the VPN.
Network reliability is a critical component of networking. Networks must keep operations and services running smoothly, without interruption. Network reliability can be classified into three categories: equipment-class, network-class, and service-class.
-Service-class reliability focuses on service management instead of network connectivity to prevent interruptions in services.
-Equipment-class reliability includes an array of technologies, such as hot-swapping, redundant backup, as well as seamless transitioning to new technologies. Such technologies enable users to deploy network components in redundant mode without service interruption and ensure that when devices are faulty, services are not interrupted even if faults reach the control layer.
-Core network devices typically require carrier-class reliability. Huawei core network devices offer carrier-class reliability.
Device-class routers add reliability with the following methods:
Main control unit: 1:1
Exchanging network: 1+1 or 1:1
DC power supply: 1+1; AC power supply: 1+1 or 2+2
Fan: modularized fan design (high-performance fans provide single-point failure prevention)
Power-free backplane that features high reliability
Independent device monitoring and main control decoupling units
Hot-swappable modules
Comprehensive alarm functions
Device management unit: 1:1
To further enhance network reliability, the solution deploys devices and links in redundant mode to guarantee network-class reliability and incorporates 3-layer routing, Equal-Cost Multi-Path routing (ECMP), and Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for quick fault detection. If a link or device in the network is faulty, the system quickly switches services to maintain service delivery and increase the efficiency of existing resources configured as redundant links and devices.
The core layer link is the trunk link of the network. The solution uses the redundant MSTP or SDH links to connect provincial, municipal, and county-level core nodes. The network employs a star topology to ensure carrier-class reliability and supports service switching in the core layer within 50 ms. The backbone network core routers and MAN devices are connected, and each device has two or more connected links. Backbone network core routers and municipal routers are connected in active-standby mode to ensure that links between the municipal routers and core layers are deployed in redundant mode.
Highlights
The e-Government solution from Huawei offers significant benefits to government organizations:
Virtual router technology
The solution uses virtual router technology on provincial, municipal, and county-level core routers to build a multi-plane network that can bear multiple, independent services.
Automatic management
The multi-plane network uses independent fault location and troubleshooting systems to facilitate network maintenance, management, and optimization. The solution uses the VPN policy deployment tool to simplify network management, reduce maintenance costs, and enable unified monitoring and role-based management for networks.
Seamless additions and upgrades
The solution supports rolling out new features and services with little or no impact. By using the IPv4/IPv6 dual-stacking technology, the solution maximizes return on investment, meets the requirements of sustainable development, and supports GE, 10 GE, 40 GE, and 100 GE ports.
High reliability
Optimized network architectures, reliable network backup policies, and automatic fault detection and rectification functions are just a few of the reliability features built into the Multi-Plane e-Government Extranet Backbone network solution:
-Network devices support the complete separation of the router engine and forwarding engine.
-The main control board, switch network interface card, power supply unit, and fan are deployed in redundant mode.
-The system can switch services from the active node to the standby node within 50 ms when detecting that the active node is faulty.
-The system can switch services from one network to another network within 1s.
Scalability
Network devices are easily upgraded to support network expansion as well as service growth or other future changes, which minimizes the impact of network architecture modifications on existing devices.
Cost-effectiveness
Network devices in the e-Government solution can interconnect with existing devices, device modules can be used on other devices of the same series, and existing service boards can be used, which increases the overall cost-effectiveness of the system.
