Solución de centro de datos HRSS provincial
Data centralization, resource consolidation, and information sharing play fundamental roles during the Human Resources and Social Security (HRSS) Information Communications Technology (ICT) construction. This document introduces Huawei's provincial HRSS data center solution in terms of its design, architecture, and benefits. In Huawei's solution, the provincial HRSS data center uses a zone-based, energy-efficient design and effectively connects municipal and central HRSS systems.
Requirements and Challenges
ICT construction in the Human Resources and Social Security (HRSS) industry is in full swing, with increased service types, expanded data, and complicated processes, raising requirements for data sharing and service reuse. For historical reasons, the HRSS ICT planning and standards construction at different administrative levels are not unified, leading to information blocks and duplicated construction. Information systems are independent from each other, and management rights are separated, resulting in information silos. HRSS employees in different departments must record data changes separately, leading to inconsistent data. All of these issues seriously hinder HRSS services development.
The Urban Resident Basic Medical Insurance (URBMI) and province-wide unified medical services increase requirements for province-wide ICT construction; however, in the existing network, different data and services systems cannot communicate with each other, and data and services cannot be reused.
To robustly answer the call of China's central government and enhance province-wide ICT construction, provincial governments must urgently integrate data and service resources and enhance data sharing. Upon completion, new ICT systems must help governments optimize and consolidate HRSS services and improve social security system management and service quality by addressing the following requirements:
Providing access to different HRSS service systems
Supporting inter-department and inter-service collaboration
Fully mining existing data resources through information communication
In addition, the provincial HRSS data center must use a zone-based, energy-efficient design and effectively connect municipal and central HRSS systems..
Huawei Solution
Overall Architecture
The HRSS data center solution covers the following four aspects in terms of functions:
- Services handling — processing core services and data
- Public services — providing service User Interfaces (UIs) and one-stop queries
- Resource sharing — collecting and exchanging data
- Management and decision making — functioning as a data warehouse and analyzing collected data
The service database uses clustered servers and manages all data involved in Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) services.
Application servers ensure no Single Point of Failure (SPOF) on HRSS data center systems and better support concurrent data processing using load balancing.
The storage system stores massive service data.
Portal servers centralize all subsystem UIs to enable system display customization and Single Sign-On (SSO). Portal servers must be clustered to ensure no SPOF, even at the presentation layer, and provide concurrent access to the portal.
Exchanging servers are used to deploy data collection and exchanging platform service programs. Exchanging servers must be independently deployed in cluster mode to bear massive data HRSS information system exchanging pressure.
The data warehouse stores and manages data extracted from service databases for analysis. This data provides statistical support for decision making.
The storage system stores data for the data warehouse.
Extract, Transform, and Load (ETL) servers, management tools for ETL service programs, connect service databases and the data warehouse. ETL servers do not require a large storage space and can be either independently deployed on Personal Computers (PCs) or on the same PC as the data warehouses.
On-Line Analytical Processing (OLAP) servers are used to deploy OLAP services and store Cube models. OLAP servers can be independently deployed in cluster mode or on the same PC as the data warehouses.
Zone-based Data Center Design
Generally, based on functions, the HRSS data center consists of three logical zones: production, exchanging, and decision-making. If needed, customers can refine the data center network and plan other zones, such as public service, operation management, and development and testing, based on local information system characteristics. shows the active HRSS data center topology.
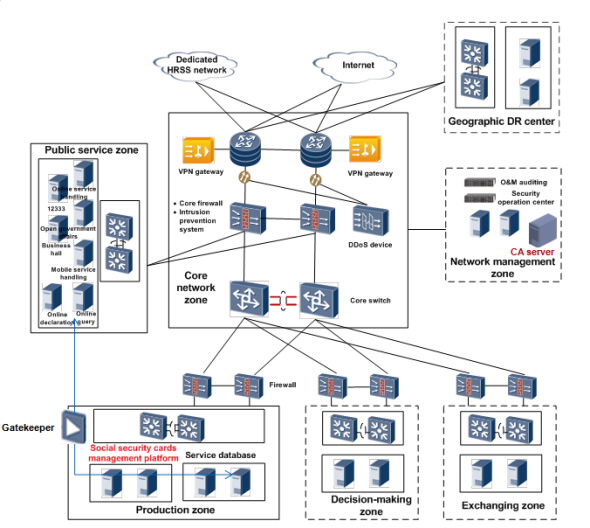
Figure 2-1 Active data center topology
The production zone directly handles services and is often deployed in the active data center. This zone includes shared resources, service resource database system, service management information system, and related hardware devices. Among the three systems, the service resource database system plays a significant role in the HRSS information system and functions as the core of counter services. In addition to data collection, service handling, and historical data storage, the service resource database system enables both local data exchanges and data exchanges between provincial and ministry-level data centers.
The production zone is configured with service database servers to provide data processing for other HRSS service systems, such as the social security card system and core social security service system. Application servers are also deployed in the production zone to process service handling requests sent from the service front end and interconnect with database servers for data processing. Additionally, application servers process applications on the non-core service systems. Storage systems are also necessary for the production zone to store massive service data.
Exchanging zone
The exchanging zone processes local services and enables horizontal and vertical data exchange and sharing. Like the production zone, it is deployed in the active data center. It includes the exchanging resource database, application software package, and related hardware devices.
The provincial social security cards exchanging database processes and filters data in the production zone and stores only data that indicates processing results. The exchanging zone backs up production zone data, supports horizontal inter-department data exchange, enables upper-level agency network scanning, and monitors local public services and funds.
In the exchanging zone, horizontal connections to the bureau of taxation, banks, hospitals, drugstores, and municipal administrative agencies, and vertical connections to provincial HRSS bureaus must be completed. Additionally, exchanging databases connected to bureaus of health, homeland security, public security, and social affairs must also be planned. To this end, standards-compliant interfaces enabling these data exchanges must be constructed.
Decision-making zone
The decision-making zone provides service data macro decision-making and includes a macro decision-making database, method library, model library, data collection and analysis software, and related hardware devices.
Provincial governments can customize dedicated database planning in the decision-making zone. Storage in this zone holds the original province-wide HRSS decision-making data.
According to Golden Insurance Projects security requirements, HRSS data center applications must be deployed based on zone requirements, and devices in different zones must be isolated. Security devices, such as firewalls, are used to secure inter-networking data exchange.
Data Center Equipment Room Design
Green data centers are a development trend and must be constructed to ensure the energy efficiency of IT devices and equipment room facilities with minimal adverse environmental impact. It must be environmentally friendly and feature energy savings, high reliability, and high availability. A green data center's basic infrastructure comprises eight systems: civil work, decoration, power supply, cooling, intelligent video surveillance, comprehensive cabling, firefighting, surge protection, and grounding systems, as shown in

Figure 2-2 Green data center main components
Solution Highlights
- The data center is divided into several zones, based on functions. Applications are grouped by application type, and devices in different zones are independently deployed or isolated. In addition to controlling inter-zone service data transmission, gatekeepers are planned to control service data flow direction, enabling a controllable data center.
- The data exchange and sharing platform uniformly provide data sharing and exchanging, ensuring production data security and service system independence.
- Applications can be migrated using the cloud platform, which sharply reduces the new IT system deployment period and saves an estimated 30 percent of devices and reduces energy consumption by an estimated 50 percent.
- HRSS data centers are uniformly operated and maintained, ensuring visual, controllable data center management.
Customer Benefits
The overall architecture of Huawei's HRSS data center solution covers several areas, including IT infrastructure, service operating system, with compliance to related standards and regulations. Huawei's solution helps provincial governments address both present and future service development requirements.
- Unified social security cards
- Service integration
- Construction of four platforms:
- Collaboration of nine subsystems:
All insured people have a nation-wide unified social security card that integrates pension, medical, unemployment, work injuries, maternity insurance, and employment services.
Human resources and social security services are integrated to achieve one-stop service handling.
Highly stable, high-speed infrastructure platform
Resource sharing and service handling platform
Function-rich, convenient public service platform
Easy-to-manage, controllable decision-making platform
These subsystems include infrastructure, disaster recovery, social insurance management, human resources management, cross-regional information exchange and settlement, public service, comprehensive service, decision-making, and social security card subsystems
