Solución de seguridad móvil AnyOffice
El sistema de Auditoría de Mantenimiento Unificado (UMA) de HUAWEI gestiona, monitorea y audita, de manera centralizada, a todo el personal que lleva a cabo tareas de operación y mantenimiento (O&M) dentro de la empresa. De este modo, se reducen los riesgos internos de O&M relativos a los dispositivos de red, los servidores, las bases de datos y los sistemas de servicios con el fin de perfeccionar los sistemas de gestión de IT de la compañía. Además, la UMA cumple con las reglamentaciones y los estándares relacionados.
Background
Statistics shows that over 70% of security events are triggered by employees, particularly maintenance personnel. The violations include unauthorized access, misoperations, abuse of privilege, and sabotage. Enterprises need a well-run IT system security audit mechanism to prevent misoperations from causing severe consequences.
As the Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) Act takes effect, enterprises have an increasing call for IT internal control. The focus of IT internal control is to control and audit administrators' operations on hosts, the network, and databases. IT internal control is faced with a dilemma that administrators granted privileges for IT maintenance can mis-operate or even tamper mission-critical data. If maintenance operations are not controlled or audited, the administrators or third-party maintenance personnel can easily access and tamper mission-critical data or configurations without anybody's knowledge.
To control risks in IT internal control, administrators granted high privileges must be audited. However, the IT departments of most large-scale organizations have difficulties in auditing maintenance operations due to organizations' complicated IT systems and large number of maintenance personnel.
In most organizations, computer-based audit technologies and tools are used to audit operations and improve work efficiency. However, the priority for the organizations is to define the audit scope. What types of information must be audited? What information or operations are critical? Current audit tools obtain data from the network or server logs. Such data contains a large amount of routine business data. It is difficult to distinguish mission-critical or sensitive data from such huge amount of business data. As a result, operations cannot be traced or examined, causing audit to be inaccurate or inefficient.
HUAWEI UMA
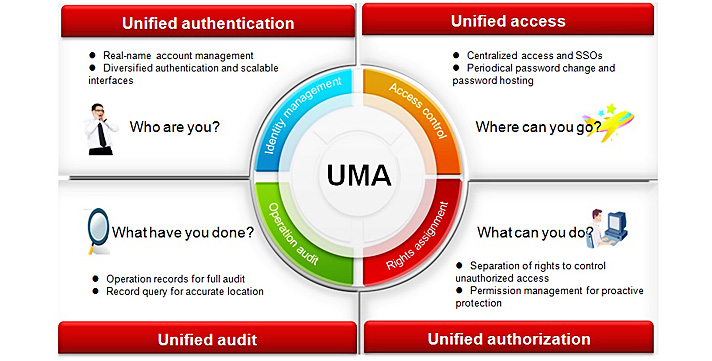
Based on the industry's best practices, regulatory compliance, and years of experience in security services and operation and maintenance (O&M) management, Huawei launched the Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA) system dedicated to the IT operation management. The UMA combines operation management and audit. It allows you to manage all maintenance operations in a centralized way and perform fine grained audit. The UMA addresses the core issue in IT O&M management. In the UMA, natural persons' authorization for resources is centrally managed. Each natural person account is correlated with a resource account in a relationship of natural person account (primary account) — resource — resource account (secondary account). The primary account used for identification is correlated with a unique secondary account used for operating resources. The UMA also records, analyzes, and presents all operations of authorized natural persons. Based on the operation records and analysis, the UMA helps you prevent incidents in advance, monitor them in progress, respond to them upon violations, and report them afterwards. The UMA also provides functions such as the track reproduction of key operations, operation intention analysis, global monitoring in real time, and operation playback.
In most cases, users of the UMA have important service systems or network infrastructures. Such users have some or all of the following requirements:
1. Mission-critical servers and network devices must be secure.
2. Maintenance personnel's permission for core assets must be clearly defined and managed in a centralized way.
3. Risks in ongoing or future internal control must be effectively controlled.
4. Encrypted SSH operations can be recorded and audited.
5. Sufficient data and methods must be provided for causal tracing.
The core value of the UMA is that this audit system improves the O&M process of business systems to meet regulatory compliance requirements within and outside organizations. This core value is demonstrated in the following aspects:
- Provides an all-in-one solution that integrates account management, resource management, single sign-on (SSO), identity authentication, access authorization, and operation audit.
- Traces attackers step by step after incidents based on detailed audit records.
- Prevents the loss of key information assets by access control.
- Changes the accounts and passwords of mission-critical servers and network devices periodically and informs administrators of the change in a safe way.
- Authenticates mission-critical server and network device entities to control user operations in a fine grained way
- Reinforces behavior monitoring on the intranet and extranet to meet internal control or regulatory compliance requirements.
The UMA provides all security functions based on the account permission management mode of user (natural person) → target device (resource) → resource account. The following details the characteristics of the UMA's security functions:
1. Centralized management: All natural persons, mission-critical servers, and core network infrastructures (including accounts stored on the infrastructures) and their SSOs are centrally managed.
2. Identity management: Accounts of natural persons and resources are correlated. Operations are managed by real name. The operator (natural person) instead of a shared account can be traced from an operation.
3. Access control: Administrators can define access control policies to assign each user appropriate network resources.
4. Permission control: Firewalls are used to restrict user permission to the command level, which effectively controls the permissions to use the root account.
5. Operation audit: Access information about all natural persons (including command inputs and outputs) can be recorded and played back. The detailed records help track attackers step by step.
Oriented to regulatory compliance in internal control, HUAWEI UMA provides powerful means to monitor and audit operations. In addition to the secure, efficient, and intuitive audit of maintenance operations on hosts, servers, network devices, and security devices, the UMA also provides detailed records on policy configurations, system maintenance, and internal access, and supports the fine grained audit and playback of full operation process. Compared with traditional audit systems, the UMA audits content instead of events. It combines identity authentication, authorization, and audit. Only legitimate users are granted the permission to maintain key resources.
The UMA is applicable to a wide range of industries that have demanding requirements on security. The industries include finance, government, telecommunication, securities, post, taxation, customs, and transportation. The UMA have the following features:
Support for various O&M environments
The UMA supports common maintenance protocols such as TELNET, FTP, SFTP, SSH, RDP (Windows Terminal), AS400, VNC, and Xwindows.
The UMA supports various mainstream operating systems such as Window, Linux, BSD, AIX, Solaris, and HP-UX and a wide range of network devices such as routers and switches from HUAWEI and Cisco, security devices, and databases such as Oracle and SQL Server.
The UMA can also record screens, digest text from videos, and identify key operations intelligently, allowing you to query and audit key operations on videos. You use the UMA to search for key operations on videos as easily as you use a search engine.
Usually, similar products from peer vendors do not support a complete set of maintenance protocols and operating systems. For example, peer products do not support the VNC, X11, and KVM, and most of them do not support AS400. With the support for various O&M environments, the UMA allows you to centrally maintain operations in various complicated scenarios on one audit system, simplifying management, reducing costs, and meeting compliance requirements.
Control, record, and audit of all operations in sessions
In the UMA, each session is recorded and controlled. The UMA records all operations performed during a session in detail and uses command files or playback files to record the full process of the session. For example, the UMA records each server maintenance session initiated by an administrator in a command file or playback file. The file keeps session details such as time, user name, source/target IP address, operations, and results. Moreover, the UMA also monitors and controls operations in a session.
Similar products from most peer vendors record only operations on texts, failing to control risky operations in real time. The UMA records operations on both texts and videos and provides you with more detailed operation processes, helping you prevent malicious operations, trace liabilities, and make maintenance visible and controllable.
As the only interface for operation maintenance, the UMA brings enormous benefits by monitoring, recording, and standardizing the full operation processes.
1. Compliant with regulations
At present, an increasing number of organizations have one or more compliance requirements. For example, companies listed in the United States must comply with regulations specified in the SOX Act; governments, government-funded institutions, and state-owned enterprises all have their own regulatory compliance. The UMA provides an independent audit solution to help you improve IT internal control and audit within organizations, meeting different compliance requirements.
2. Reduced damage and leakage of core information assets
In business systems, core information assets are usually stored on a few mission-critical systems. The UMA helps you enhance the audit and access control of the mission-critical systems, remarkably reducing the damage and leakage of core information assets.
3. Effective control of O&M risks, causal tracing, and accountability
Maintenance personnel in the O&M department of an organization are granted all user rights (root account and password) for system and network device management. This permission assignment is highly risky because any misoperation or sabotage of the maintenance personnel may cause severe consequences. Additionally, the maintenance personnel use the same account in system maintenance. Therefore, it is difficult to figure out the person who performs a specific operation. To address this problem, the UMA provides the role-based access control and audit to identify maintenance personnel, remarkably lowering O&M risks and facilitating causal tracing and accountability.
4. Independent audit and separation of usage, management, and monitoring rights, delivering a well-run IT internal control process
In a well-run IT internal control process, the rights to use, manage, and monitor IT systems must be separated. Audit performed on the basis of separated rights enables better control of risks in business and maintenance operations. The UMA assigns the usage, management, and monitoring rights to different maintenance personnel, helping you build a well-run IT internal control process.
| Model | UMA Standard Edition | UMA Enterprise Edition |
|---|---|---|
| Intended customer | Small- and medium-sized enterprises | Large-sized enterprises |
| Hardware appearance |
Host
(Optional) APPBOX |
Host
(Optional) APPBOX
|
| Host specifications | Height: standard 2 U rack CPU: 1 x Intel quad-core E5-2403 Memory: 1 x 8 GB Power supply and fan: 1+1 redundant power supplies and fans System disk: 2 x 300 GB SAS in RAID 1 mode Data disk: 2 x 2 TB SATA in RAID 1 mode (scalable to 12 x 2 TB) Network ports: onboard 6 x GE ports (scalable to 14 GE ports) |
Height: standard 2 U rack CPU: 2 x Intel quad-core E5-2403 Memory: 2 x 8 GB Power supply and fan: 1+1 redundant power supplies and fans System disk: 2 x 300 GB SAS in RAID 1 mode Data disk: 2 x 2 TB SATA in RAID 1 mode (scalable to 12 x 2 TB) Network ports: onboard 8 x GE ports (scalable to 14 GE ports) |
| APPBOX specifications | Height: standard 2 U rack CPU: 1 x Intel quad-core E5-2403 Memory: 1 x 8 GB Power supply and fan: 1+1 redundant power supplies and fans System disk: 2 x 300 GB SAS in RAID 1 mode Data disk: 2 x 2 TB SATA in RAID 1 mode (scalable to 12 x 2 TB) Network ports: onboard 4 x GE ports (scalable to 14 GE ports) |
Height: standard 2 U rack CPU: 1 x Intel quad-core E5-2403 Memory: 1 x 8 GB Power supply and fan: 1+1 redundant power supplies and fans System disk: 2 x 300 GB SAS in RAID 1 mode Data disk: 2 x 2 TB SATA in RAID 1 mode (scalable to 12 x 2 TB) Network ports: onboard 4 x GE ports (scalable to 14 GE ports) |
| Concurrent connections | Character terminal: 500 Graphic terminal: 200 |
Character terminal: 1000 Graphic terminal: 300 |
| Number of managed devices | 50/100/200/300 | 500/1000/more (clustering) |
| Types of managed devices | Router, Switch, Firewall, Windows/Linux/Unix Servers (any vendor) | |
| Types of managed applications | UMA host supports: Character terminals such as telnet and SSH Graphic terminals such as RDP, X11, and VNC APPBOX supports: Web-based operations such as HTTP and HTTPS Databases including Oracle, DB2, Sybase, SQLServer, Informix, MySQL, and PostgreSQL Remote graphic control tools including pcAnywhere, Radmin, DameWare, ESXI, and AS400 KVMs including Avocent, Ranitan, and ATEN Other private O&M systems such as U2000 network management system | |
| User management | User permission level setting, account lifecycle management, user group, and batch user import | |
| Authentication management | Local authentication, Radius authentication, AD domain authentication, certificate authentication, and open extended authentication system | |
| Device management | Management at device, device group, and device account levels Single modification, periodic authentication, and automatic fill-in and delivery of account passwords | |
| Permission management | Permission is granted to users by device IP, protocol type, or account password. Devices are accessible to administrators who have permission to manage the devices. Permission assignment by device group or user group | |
| Security audit | Playback of command-line operations, graphics and videos, keyboard commands, and operation logs Summary of graphic operations in text for intelligent operation identification Risky command policy creation and automatic identification and interruption of risky command execution Real-time monitoring and interruption of user operations | |
| Deployment mode | Out-of-band deployment with no change to original network structure Single-host, dual-host, clustered, and tiered deployment | |
Liability Tracing for Shared Accounts of High Privileges
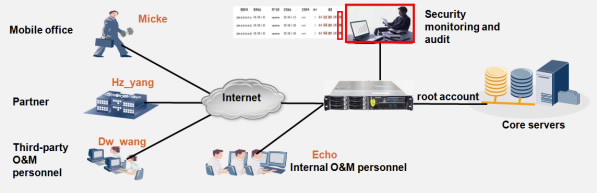
Challenges
In traditional O&M, all maintenance personnel including mobile office staff, partners, third-party maintenance personnel, and internal maintenance personnel use a shared account of high privileges (such as the root account) to log in to and manage mission-critical servers. After mission-critical data is tampered or illegal commands are executed, system logs record only the accounts that perform the operations. The specific personnel (natural person) who performed illegal operations cannot be found.
Benefits
The UMA allows you to easily trace reliabilities and handle incidents. The UMA assigns each natural person (maintenance personnel) a primary account (audit account) and a secondary account (root account used to log in to mission-critical servers). A primary account is correlated with only one secondary account. System logs record secondary accounts that perform operations. After an incident occurs due to illegal operations, you quickly find the violator by checking primary accounts and learn about operation details such as login time, actions, and results.
Fine Grained Control of Maintenance Operations
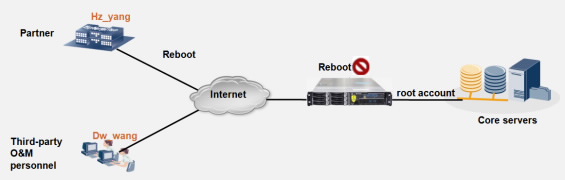
Challenges
In traditional O&M, a high-privilege account (such as a root account) has full rights to a system. Misoperations or sabotage performed using such an account may cause irretrievable consequences.
Benefits
The UMA allows you to control the permissions granted to each maintenance personnel (operator). In the UMA, an operator is assigned a primary account (for identification) and a secondary account (for maintenance). Operation permissions of the operator are determined by the primary account. For example, if the primary account of the operator has no permission to reboot the system, the operator cannot reboot the system even if using the secondary root account that has this permission. This permission control function effectively prevents misoperations and unauthorized operations, ensuring high system availability.
Third-Party O&M Monitoring
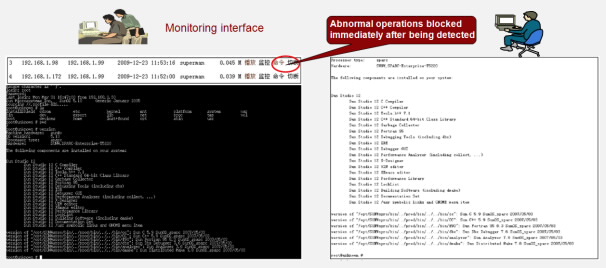
Challenges
Most large-scale organizations entrust the maintenance work to third-party agents or companies. Third-party maintenance personnel usually act in excess of authority, for example, viewing confidential information and performing unauthorized operations.
Benefits
The UMA allows you to restrict the operation scope of third-party maintenance personnel to ensure correct maintenance. In the UMA, you can monitor third-party operations in real time and at the same time control the operations. For example, you can cancel an unauthorized operation.
Compliance Audit
Challenges
With the application of the service-oriented architecture (SOA), COSO's Internal Control — Integrated Framework and other internal control standards are widely accepted by industries. Still, more industry standards on internal control and risk management come into force. The standards include the code for internal control audit, internal control guidelines for commercial banks, securities traders, insurance companies, listed companies, and state-owned enterprises, and guidelines for compliance risk management. These standards all require organizations to audit their IT system O&M.
Benefits
The UMA provides a complete set of audit means specific to organizations' IT operation risk control, internal control security, and regulatory compliance. In addition to the secure, efficient, and intuitive audit of maintenance operations on hosts, servers, network devices, and security devices, the UMA also provides detailed records on policy configurations, system maintenance, and internal access, and supports the fine grained audit and playback of full operation process.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| 1.1 | Device |
| UMA-1C8G | UMA Platform Standard Edition, 1*Quad-Core CPU, 8 GB Memory, with HW Storage Node Baseboard Management Software |
| UMA-2C16G | UMA Platform Enterprise Edition, 2*Quad-Core CPU, 16 GB Memory, with HW Storage Node Baseboard Management Software |
| UMA-APPBOX | UMA APPBOX, with HW Storage Node Baseboard Management Software |
| 1.2 | Software License |
| LIC-UMA-50-EN | Software Operation, Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA) English Edition, 50 Licenses, Electronic License |
| LIC-UMA-100-EN | Software Operation, Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA) English Edition, 100 Licenses, Electronic License |
| LIC-UMA-200-EN | Software Operation, Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA) English Edition, 200 Licenses, Electronic License |
| LIC-UMA-300-EN | Software Operation, Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA) English Edition, 300 Licenses, Electronic License |
| LIC-UMA-500-EN | Software Operation, Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA) English Edition, 500 Licenses, Electronic License |
| LIC-UMA-1000-EN | Software Operation, Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA) English Edition, 1000 Licenses, Electronic License |
| LIC-UMA-Cluster-EN | Software Operation, Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA), Cluster License, Electronic License |
| LIC-UMA-HA-ST | Software Operation, Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA), Standard Edition License, Electronic License |
| LIC-UMA-HA-TO-EN | Software Operation, Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA), Upgrade to Enterprise Edition License, Electronic License |
| LIC-UMA-APPBOX1-EN | Software Operation, Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA), APPBOX License, Electronic License |
| LIC-UMA-APPBOX2-EN | Software Operation, Unified Maintenance Audit (UMA), APPBOX Enhanced License, Electronic License |