| Function
|
Specifications
|
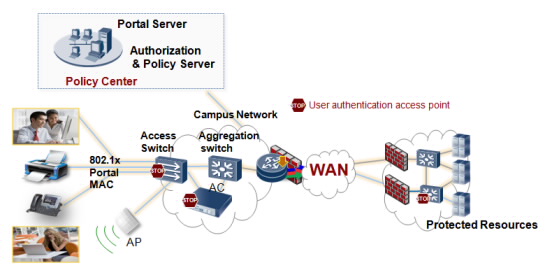
| Identity authentication
|
System-based account authentication
|
| Windows Active Directory (AD) authentication
|
| Third-party LDAP authentication
|
| Mobile certificate authentication
|
| Anonymous authentication: allows terminal users in a network area to access the intranet without any passwords.
|
| Policy Engine
|
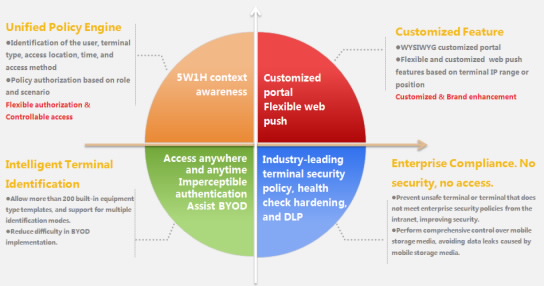
Provides 5W1H-based context awareness (identification of user identities, terminal types, access locations, access time, and access modes) access control and role- and context-based policy authorization.
Pushes services based on multiple factors, such as terminal IP addresses, APs, and SSIDs.
Supports portal customization.
|
| Network access control
|
Compliance check: Security assessments and system configurations prevent non-compliant terminals from accessing the protected resources.
|
| Automatic isolation of non-compliant terminals and one-click repair for terminal faults
|
| User-based access authorization: denies unauthorized access.
|
| Guest access lifecycle management
|
Supports self-service account application for visitors and employees.
|
| Notifies visitors of account credentials through Web pop-ups, emails, and SMS.
|
| Offers APIs for guest account creation, deletion, modification
|
| Supports the customization of guest account registration and login pages
|
| Terminal Identification
|
Identifies PCs, Mobile phones, and IP phones.
|
| Identifies the Windows, Linux, iOS, Android, and Mac OS operating systems and their versions.
|
| Supports various information types and measures, such as DHCP, RADIUS, HTTP, MAC OUI, and SNMP scanning.
|
| Security management
|
Security hardening: Static configuration check (antivirus software, patches, suspicious registries, suspicious processes, and illegitimate software) and dynamic audit (port use, enabling least services, peripheral access, ARP detection, and traffic monitoring) to discover and eliminate security threats
|
| Office behavior management: Covers web access, media download, and non-office software installation.
|
| Information leak prevention: The TSM system manages peripherals and mobile storage devices, restricts illegitimate Internet access, and controls network applications.
|
| Network protection: The TSM system isolates the traffic from legitimate and illegitimate terminals to prevent them from becoming attack sources.
|
| Desktop management
|
Patch management: The TSM system provides professional patch management for one-stop patch check and recovery. You can view information about patch deployment by device or patch. The TSM system can collaborate with the WSUS.
|
| IP asset auto-discovery: The TSM system automatically discovers non-applicable devices, such as IP printers, IP phones, smart phones, cash registers, and bar code scanners.
|
| Asset lifecycle management: The TSM system prevents the loss of software and hardware assets, and provides real-time visibility of corporate assets.
|
| Software distribution: The TSM system uses the distributed storage and express forwarding technologies for delivering large files on the intranet. These technologies have low bandwidth requirements and are highly efficient.
|
| Remote desktop assistance
|
| Message announcement: The TSM system pushes bulletin messages to specific users or departments. You can set the validity period of bulletin messages.
|
| Policy management
|
Hierarchical and domain-based management: The TSM system ensures that administrators manage different services in different departments.
|
| Policy template: You can configure policies and set parameters in one policy template. Different users or departments can reference the same policy template.
|
| Location awareness: Appropriate security policies are applied to terminals at different locations.
|
| You can define or obtain policies from the security center.
|
| Maintainable report
|
Predefined report templates
|
| Predefined trend reports
|
| You can define or obtain reports from the security center.
|
| System management
|
System status monitoring: When an anomaly occurs on the server, the TSM system generates alarms, including dialog box alarms and email alarms.
|
| Online client fault diagnosis: The TSM system diagnoses and rectifies all faults on the managed clients.
|
| Remote database backup
|
| Networking mode
|
Centralized networking: This mode applies to small networks.
|
| Distributed networking: This mode applies to large networks or networks with many branches.
|
| Hierarchical networking: This mode applies to large networks that require multiple TSM systems.
|